
Knowing how to prompt generative artificial intelligence has rapidly become an essential skill in education and the workplace. As students and professionals adopt tools like ChatGPT, Claude and other large language models, a new literacy is emerging: the ability to write effective prompts that produce clear, accurate and useful outputs. Yet, many colleges may not be keeping pace with this shift.
To better understand the state of AI prompt literacy, a nationwide questionnaire among 500 college students, including traditional and nontraditional learners, was conducted on behalf of Northern Kentucky University (NKU). For this study, nontraditional students were respondents who identified as part-time students, online learners, returning adult learners, parents or caregivers while studying, or individuals who changed careers or returned to school later in life. Traditional students were those who identified as full-time students only. The findings show that most students are teaching themselves how to use AI systems, suggesting a growing gap between classroom instruction and the demands of an AI-driven economy.
Key Takeaways
- 71% of college students reported teaching themselves AI prompt writing using tools like ChatGPT.
- 40% of college students said they would enroll in an AI prompt-writing course if their college offered one.
- 65% of college students have used AI prompts to draft resumes, cover letters or prepare for interviews.
- 54% of college students believe that being skilled in AI prompt writing will improve their chances of getting hired in their field.
- 25% of students have seen AI skills listed as job requirements, and only 18% said their school offers AI prompt-writing or AI literacy courses.
Where Students Are Learning to Write AI Prompts
Prompt writing has become a new aspect of learning experiences in higher education. As artificial intelligence reshapes academics, students are learning to interact with AI systems through experimentation and self-guided study.
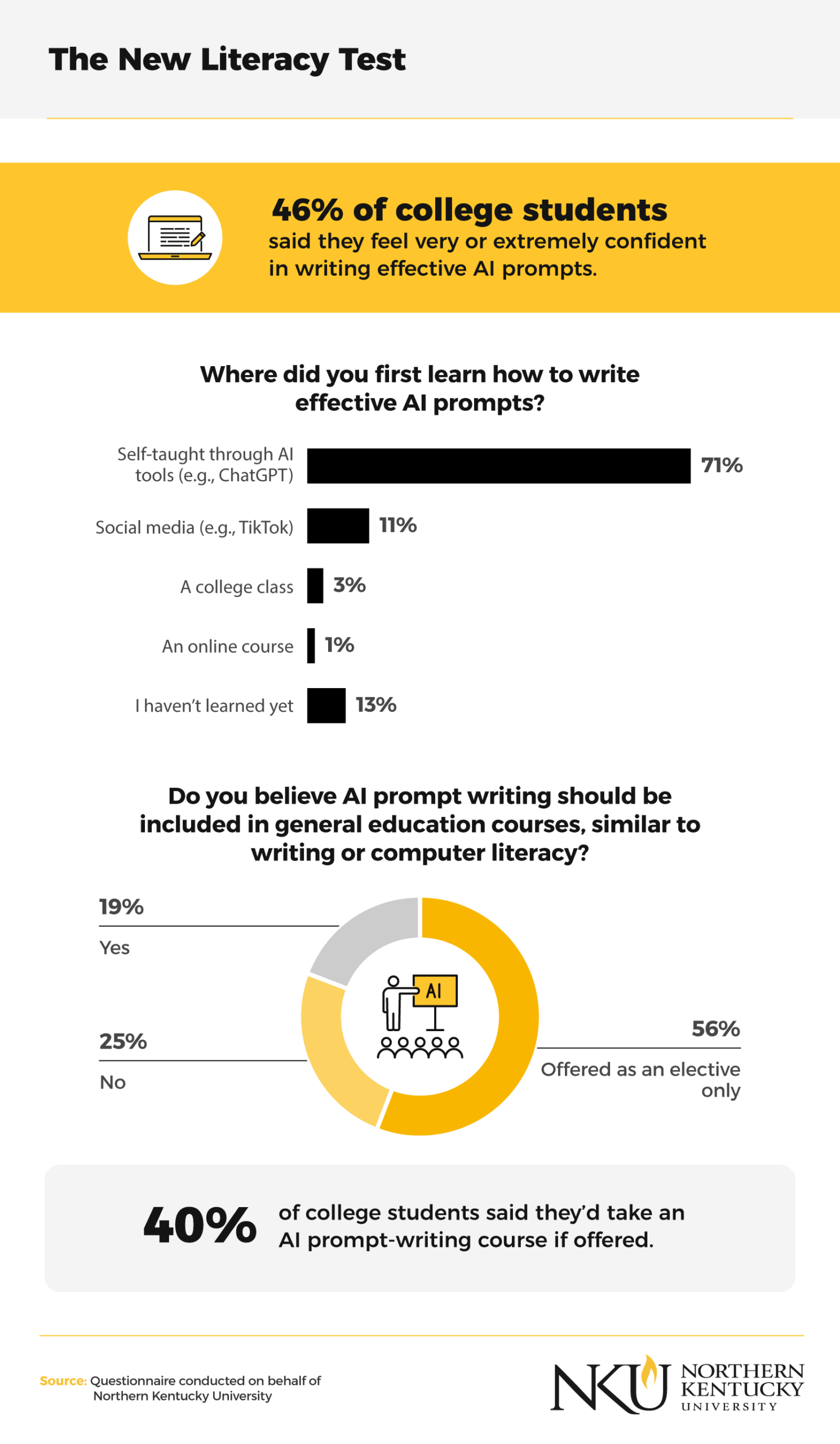
When asked how they learned to write effective AI prompts, most students (71%) reported teaching themselves by using generative AI tools like ChatGPT. This self-taught approach reflects the adaptability of learners in higher education, but it also underscores the need for structured instruction.
Only 18% of students said their college offers AI prompt-writing or AI literacy courses, while 42% said they were unsure, and 41% said they definitely don’t. Many students were interested in an official class, with 40% saying they would enroll in a course focused on prompt writing if their college offered one.
Nearly half of nontraditional students (48%) said they feel very or extremely confident in their ability to write detailed prompts, compared to 44% of traditional full-time students. The data suggests that online learners may be developing stronger AI competencies through self-paced exploration of genAI tools. However, without formal coursework, many students risk missing foundational knowledge about AI models and the responsible use of AI-generated content.
How Prompt Writing Boosts Job Prospects
As generative AI becomes embedded across industries, the ability to communicate effectively with AI tools has evolved into a professional development skill. Mastering prompt literacy now offers students a competitive advantage in demonstrating adaptability and digital fluency to employers.
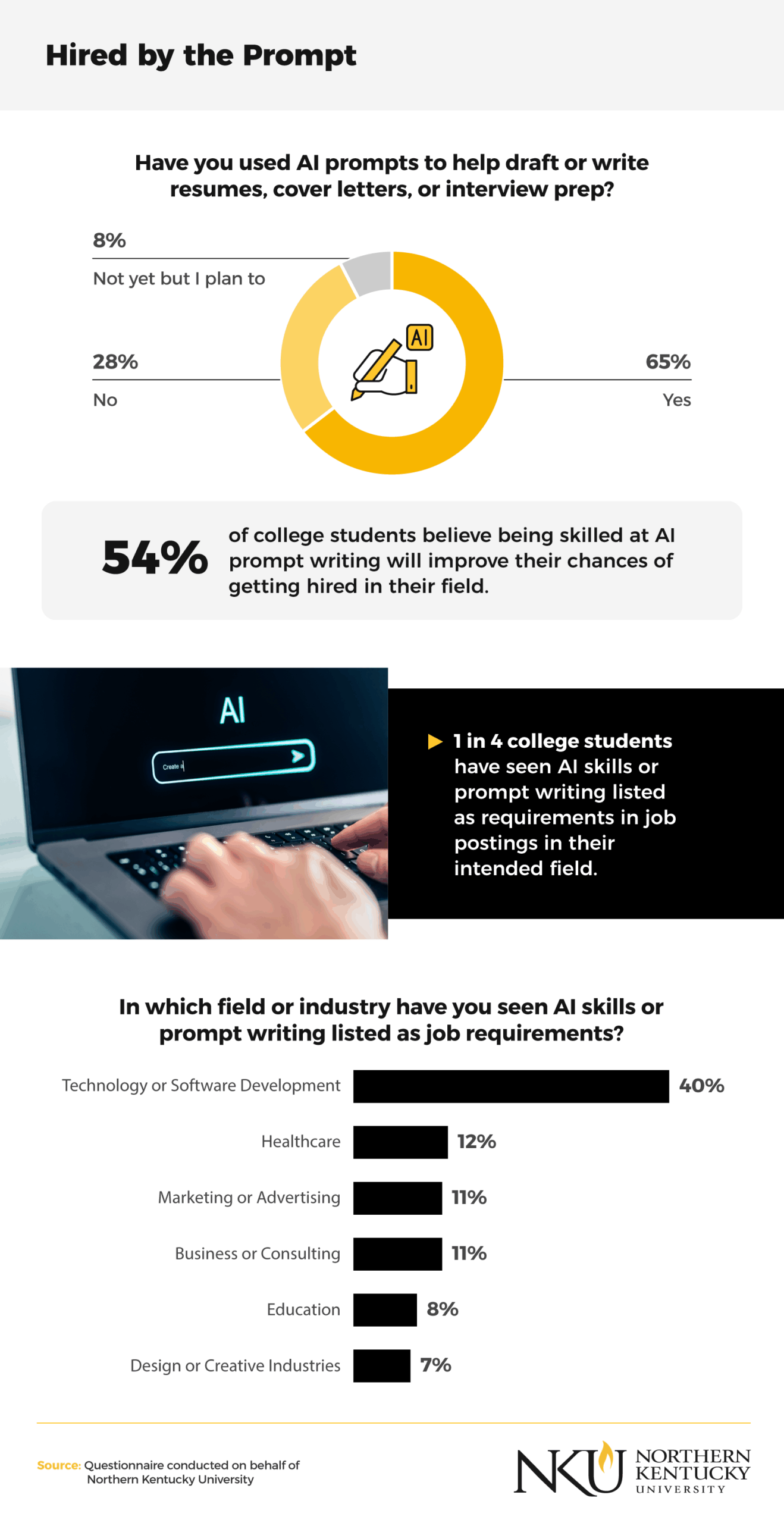
Sixty-five percent of college students have already used AI prompt writing to draft resumes and cover letters or to practice for interviews. More than half (54%) believe that skillful use of generative AI tools will improve their employability.
Students in technology, healthcare and software development were especially likely to report seeing AI prompt writing listed as a desired skill on job postings. Overall, one in four college students had noticed AI prompt-related requirements in their intended field. As generative AI models become integrated into workplace software and chatbot systems, the ability to communicate clearly with AI through structured prompts will become a fundamental component of professional development.
A Practical Guide to Teaching and Learning AI Prompt Writing
As AI becomes central to both academic and professional work, students and educators alike must develop practical skills for writing effective prompts. Building prompt literacy not only strengthens critical thinking and problem-solving skills but also helps learners use generative AI tools responsibly and confidently in higher education settings and beyond.
For Students
Students can enhance their prompt literacy through free, high-quality resources that support skill development in artificial intelligence and effective prompt writing.
- Explore the free open-source courses from Learn Prompting, which cover prompt engineering fundamentals for generative AI tools like OpenAI’s GPT
- Try the Google Prompting Essentials course through Grow with Google, which offers five short lessons on creating reusable, effective prompts.
- Use NKU’s Student Guide to AI to learn how to navigate academic work in the artificial intelligence era, including examples of good prompts and strategies for responsible use.
For Educators
Faculty across in-person and online programs can embed prompt-writing instruction directly into coursework to help students develop real-world AI skills.
- Incorporate prompt-iteration and feedback cycles into assignments, encouraging students to refine inputs and evaluate AI outputs. Research indicates that prompt-writing instruction enhances students’ AI self-efficacy and performance.
- Leverage NKU’s AI Resources Portal to access curated AI tools, teaching strategies and institutional policy frameworks.
- Adopt clear syllabus language for AI tool use.
These initiatives demonstrate how higher education can help students gain competencies in AI-assisted writing. By integrating generative AI instruction into writing, communications and technology courses, colleges can ensure that learners graduate prepared to use AI systems effectively and ethically.
Building the Future of AI Literacy Through Prompt Writing
As advancements in generative AI work reshape classrooms and workplaces, prompt literacy is becoming as essential as traditional writing skills. Learning how AI tools interpret language through large language models (LLMs) and machine learning systems empowers students to think critically and communicate more effectively with technology.
Writing a strong ChatGPT prompt, for example, requires the same critical thinking skills that define academic success. Students must summarize complex ideas, identify their desired outcome and design clear instructions for AI to follow. Many are now experimenting with example prompts and templates that mirror the iterative process used in natural language processing research and professional AI applications.
A well-developed prompt library not only improves consistency but also teaches learners to refine their reasoning and evaluate AI-generated outputs with accuracy and context. By understanding how AI transforms input into meaning, students and educators can harness LLMs responsibly, bridging human creativity with technological precision. As higher education adapts to this new frontier, teaching prompt literacy will help students move beyond using AI as a shortcut and instead use it as a tool for deeper learning, reflection and innovation.
Methodology
A questionnaire was administered to 500 college students on behalf of NKU to examine how college students are learning to use AI tools like ChatGPT. The sample included respondents who identified as traditional, full-time only students and nontraditional students who identified as part-time students, online learners, returning adult learners, parents or caregivers while studying, or individuals who changed careers or returned to school later in life. Data was collected in November 2025. Because this was a non-probability, online sample, results should be considered non-scientific and exploratory and are not intended to represent all U.S. college students.
About Northern Kentucky University
Northern Kentucky University offers flexible, fully online degree programs designed to prepare students for emerging fields and future-focused careers. NKU’s online Master of Science (M.S.) in Cybersecurity program equips professionals to protect data, networks and systems in an era of growing digital threats. As technology continues to evolve, NKU remains committed to providing accessible, career-relevant education for today’s learners.
Fair Use Statement
Information from this article may be shared or cited for noncommercial purposes only. When referencing or redistributing content, please include proper attribution and a working link to the original source.